Muscular System Of A Hydra
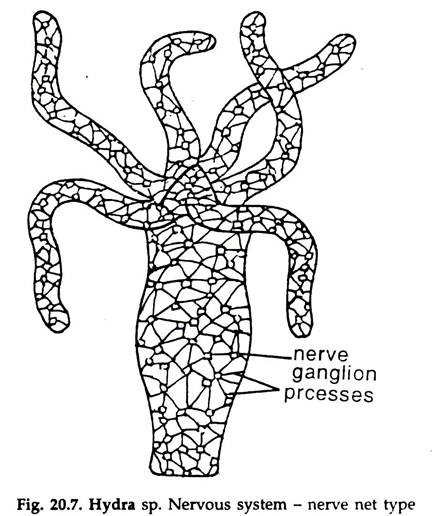
Muscular system of a hydra. Hydra s hows the movement of the following types. Hydra - Surprisingly there are many known facts about the endocrine system in hydra. A few hundred to a few thousand branching nerve cells that control their muscular movement.
Charles Stainback Alfred Musto Hunter LaGrassa. Home Tanpa Label Muscular System Of Hydra - Figure 4 From Chemical Anatomy Of Hydra Nervous System Using Antibodies Against Hydra Neuropeptides A Review Semantic Scholar All the movements of hydras are due to contractions of the epidermal muscle fibers largely as their gastrodermal muscle fibers are less. The muscles of cnidarians are comprised of epitheliomuscular cells.
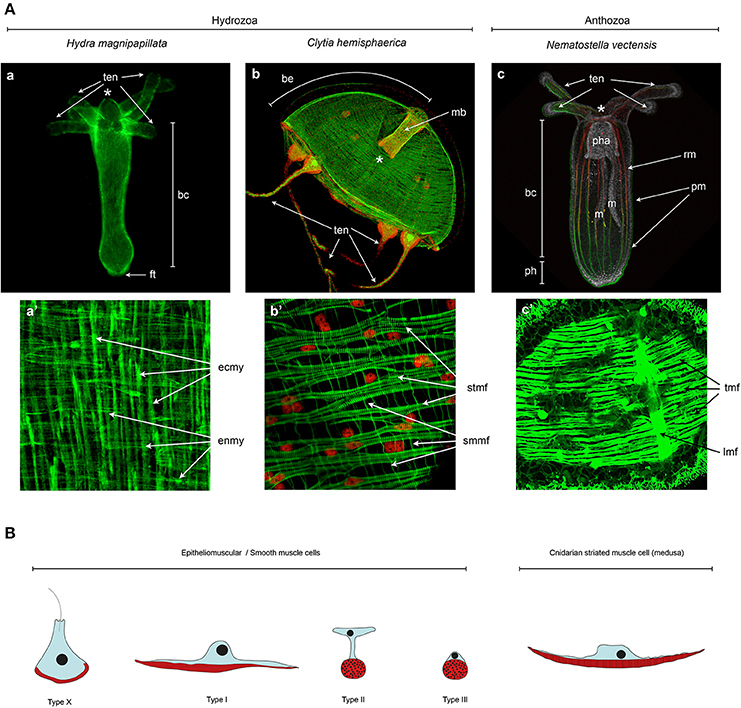
Hydra ectodermal and endodermal epitheliomuscular cells display respectively longitudinally and circularly oriented processes called myonemes Figures 4Aaa. Between the epithelial-muscular cells are groups of small rounded with large nuclei and a small amount of cytoplasm of cells called intermediate. 1 contractile functions to assist with locomotion and 2 intracellular food digestion.
Schneider 1890 states that gastrodermal and epidermal fibers have exactly the same appearance except that the gastrodermal are somewhat finer. A The hydra has a long single tentacle containing numerous nematocysts. In Hydra the pedal disc is thickly populated beset with glandulo-muscular cells and they have muscular basal extensions Fig.
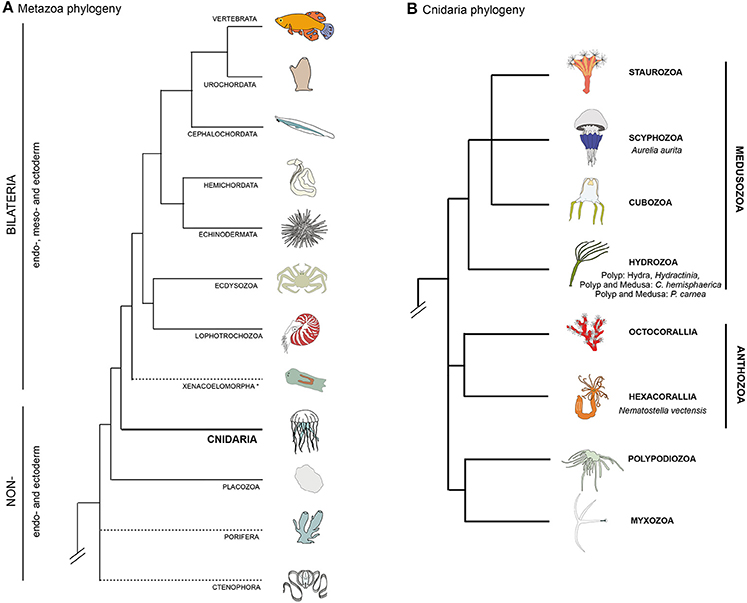
B The hydra has a single polyp that is filled with gas and keeps the organism afloat. Scientists have established the structure of their nervous system. Hydra have a circulatory system that is similar to jellyfish.
These hydrozoans are collectible and they are located in a colony. The muscles are arranged in longitudinal and circular arrangements allowing for a. In Hydras muscular and nervous systems alike these patterns appear to emerge from the coordination of many cells working in unison.
C The hydra is bell shaped and has. Ectodermal epitheliomuscular cells of Hydra are large columnar or cuboidal cells bearing two long myonemes oriented along the oral-aboral axis David 1973.
Charles Stainback Alfred Musto Hunter LaGrassa.
In Hydra the pedal disc is thickly populated beset with glandulo-muscular cells and they have muscular basal extensions Fig. They have a fluid filled gastrovascular cavity where nutrients are absorbed. Scientists have established the structure of their nervous system. Hydra have a circulatory system that is similar to jellyfish. Some granular epidermal cells of the basal disc secrete a gas to form a bubble by which the Hydra breaks from its attachment and is lifted up. In the gastro dermis they secrete digestive ferments. If Hydra are alarmed or attacked the tentacles can be retracted to small buds and the body column itself can be retracted to a small gelatinous sphere. Hydra have a circulatory system that is similar to jellyfish. In addition epi- thelio-muscular cells are joined to cnido- blasts by desmosome-like junctions Slaut-.
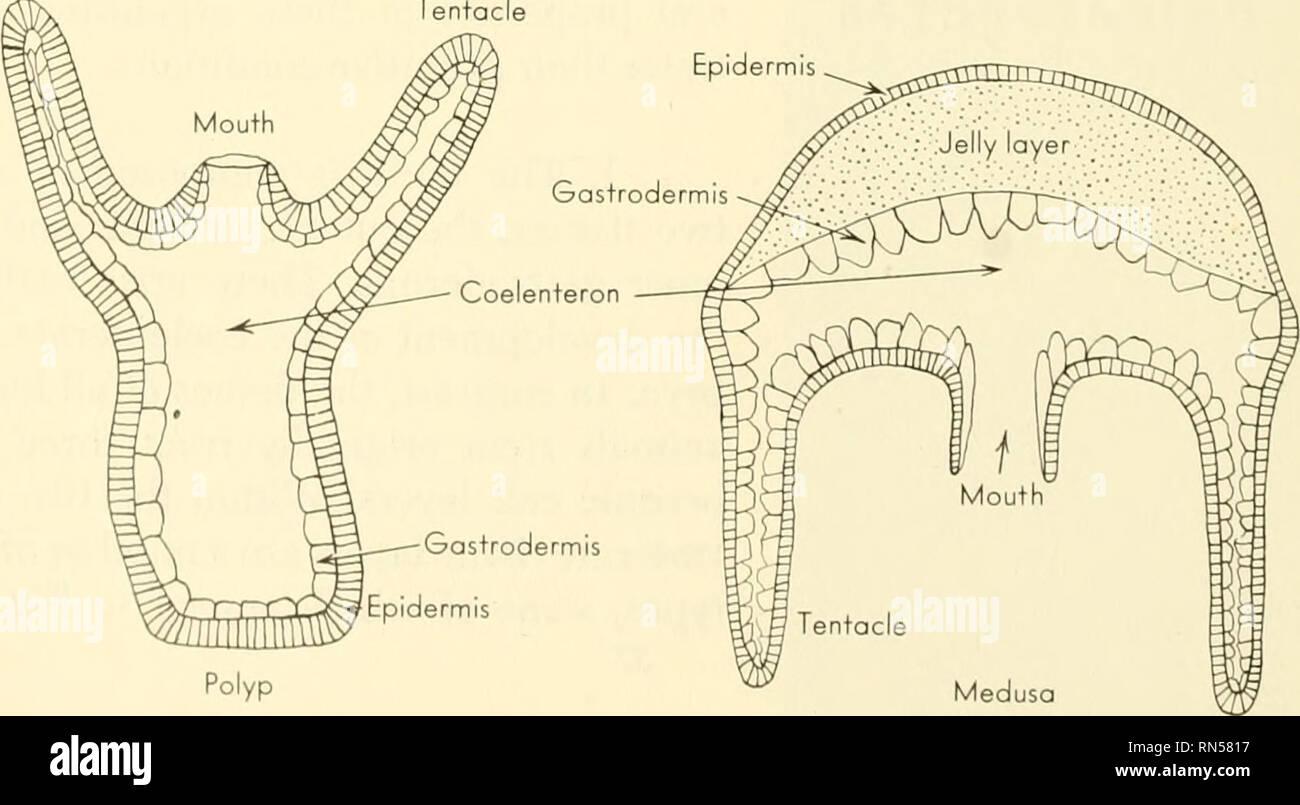
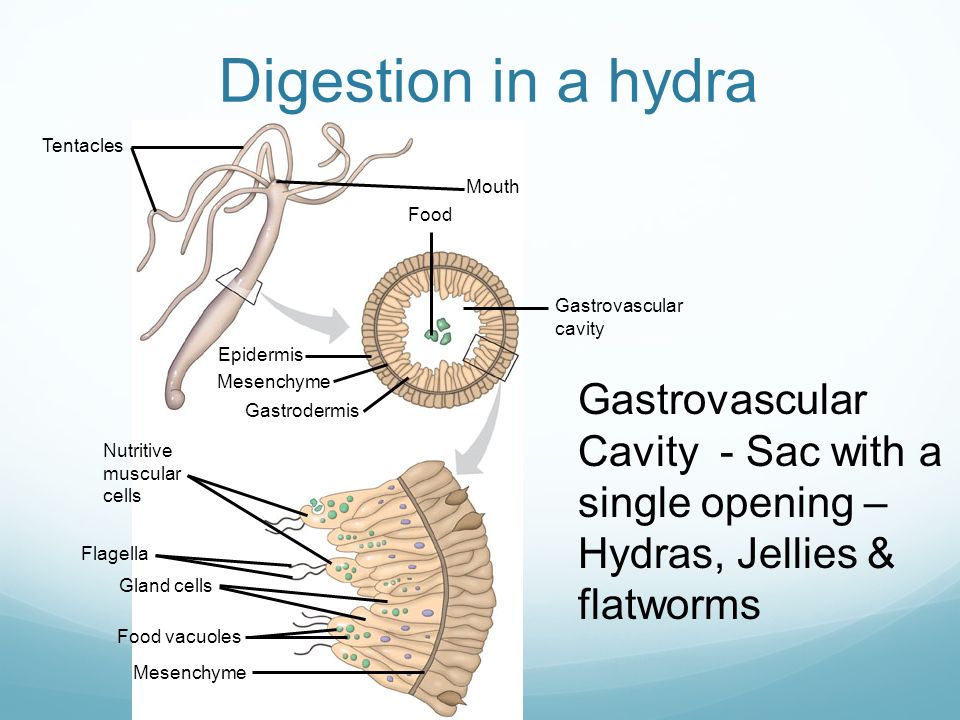
Due to muscular fibrilslying at the base of each cell the body of the hydra can contract lengthen and bend. The bulk of the animal is hollow containing the fluid-filled gastrovascular cavity enteron which functions both as a gut and as a hydrostatic skeleton against which the muscular cells of the body-wall can operate. The hydra gets it oxygen from the water that entered the cavity and it gets rid of carbon dioxide through this. A The hydra has a long single tentacle containing numerous nematocysts. The epidermal cells of the basal disc are granular and they secrete mucus for attachment of Hydra. Cnidarian muscles serve two purposes. THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM Although the two muscle layers of hydra have long been familiar there is little detailed information on the fibers.
































Post a Comment for "Muscular System Of A Hydra"